Abstract
- Hyperfine is a benchmarking instrument that runs instructions a number of occasions for correct averages.
- Hyperfine is user-friendly and permits outcomes to be exported in Markdown or JSON codecs for additional evaluation.
- You need to use Hyperfine to match program effectivity, optimize code, and automate benchmarking.
If you might want to understand how quick it runs, Hyperfine will let you know. This user-friendly, versatile instrument obtainable on Linux takes all the trouble out of benchmarking.
What Is Hyperfine?
Hyperfine is an open-source benchmarking instrument for Linux, macOS, and Home windows. Like the time command, which is out there in most distros and shells, hyperfine will measure the period of time it takes to run a program:
On the floor, hyperfine does the identical job as time, with prettier output. However the instrument has a number of benefits; Hyperfine:
- Runs a command a number of occasions, producing extra correct averages.
- Can check and evaluate a number of instructions without delay.
- Accounts for caching, outliers, and the impact of shell spawning on outcomes.
- Can export leads to Markdown or JSON codecs for additional evaluation.
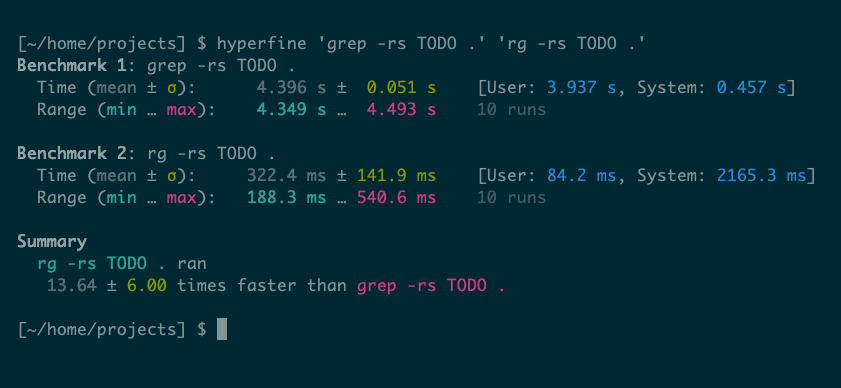
Hyperfine is especially helpful while you’re writing your individual packages. You possibly can attempt optimizations, check them utilizing Hyperfine, and replace your code accordingly. However you can even use it to decide on between completely different packages, like grep vs. ripgrep for instance:
The way to Set up and Use Hyperfine
Written in Rust, Hyperfine is a extremely moveable command that comes with man pages and fashionable command-line options like long-form choices and tab completion.

Associated
Why You Should Learn Rust, Especially If You’re New to Programming
Rust is among the latest programming languages, and it might probably change the way you see code.
Set up
Hyperfine packages can be found for a lot of Linux distributions and different OSes.
On Ubuntu, you may set up Hyperfine from a .deb launch, e.g.
wget https://github.com/sharkdp/hyperfine/releases/obtain/v1.19.0/hyperfine_1.19.0_amd64.deb
sudo dpkg -i hyperfine_1.19.0_amd64.deb
Examine the undertaking’s GitHub page for the newest launch in your structure.
On Fedora, you should utilize the dnf package deal supervisor to put in Hyperfine with a easy command:
dnf set up hyperfine
On macOS—or one other system that helps it—you can use Homebrew:
brew set up hyperfine
For different methods, examine the undertaking’s detailed installation instructions.
Primary Use of Hyperfine
Hyperfine spawns a subshell to run the instructions you move it. You don’t want to consider this an excessive amount of, however it does imply you need to run Hyperfine as follows:
hyperfine command-in-pathhyperfine /full/path/to/command
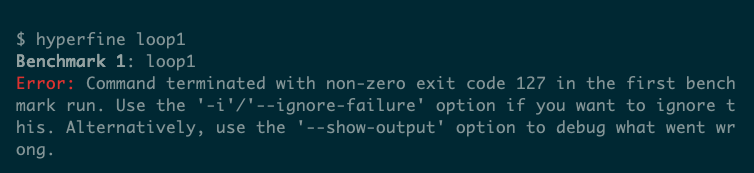
Particularly, this implies which you could’t simply run Hyperfine towards a program in your present listing by passing its title as an argument:
hyperfine a.out
Should you do that, you’ll get an error like “Command terminated with non-zero exit code 127,” which may be tough to debug.
As a substitute, simply move a path to the command, e.g.
hyperfine ./a.out
For related causes, it’s finest to cite your instructions:
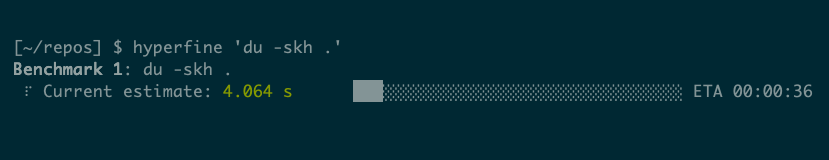
hyperfine "du -skh ~"
How Benchmarking With Hyperfine Can Assist You
Benchmarking may be as correct as you select to make it, whether or not you’re advertising and marketing a product, arguing for a code change, or merely fascinated about how rapidly you may run grep throughout your laborious drive.
Checking the Effectivity of Your Code
Hyperfine is nice at evaluating outcomes from two variations of a program below the identical circumstances. Utilizing it, you may refine your program logic and optimize your code.
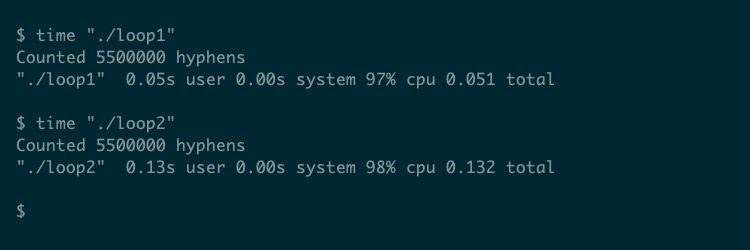
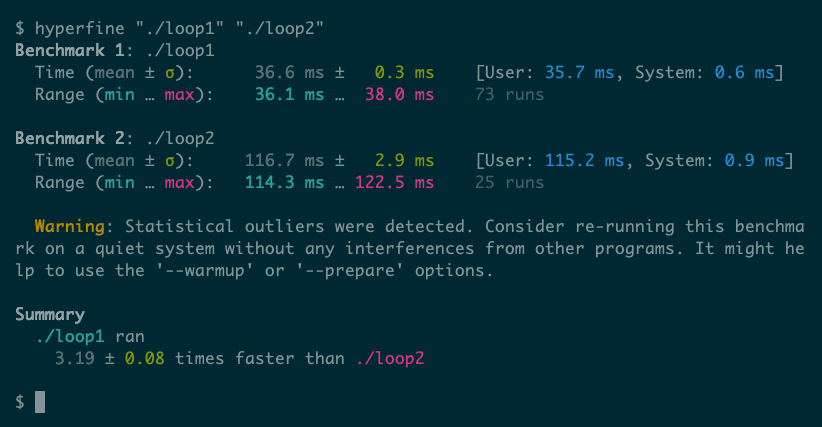
Our article on the Linux time command consists of two pattern C packages that you should utilize to display this idea. The primary, loop1.c, iterates over a string a hard and fast variety of occasions (500,000), counting the variety of hyphens:
#embrace "stdio.h"
#embrace "string.h"int major() {
char szString[] = "how-to-geek-how-to-geek-how-to-geek-how-to-geek";
int i, j, len = strlen(szString), rely = 0;
for (j = 0; j < 500000; j++)
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
if (szString[i] == '-')
rely++;
printf("Counted %d hyphensn", rely);
}
The second, loop2.c, could be very related, however it calls strlen() straight within the loop situation:
#embrace "stdio.h"
#embrace "string.h"int major() {
char szString[] = "how-to-geek-how-to-geek-how-to-geek-how-to-geek";
int i, j, rely = 0;
for (j = 0; j < 500000; j++)
for (i = 0; i < strlen(szString); i++)
if (szString[i] == '-')
rely++;
printf("Counted %d hyphensn", rely);
}
As a result of the operate name is now contained in the outer loop, strlen() runs 500,000 occasions as a substitute of simply as soon as. The time command may give fundamental details about how these two variations of the identical program evaluate:
However hyperfine provides extra element, even in essentially the most fundamental, default mode:
Timing Lengthy-Working Instructions
Though Hyperfine is especially attention-grabbing to programmers and system directors, you should utilize it in different circumstances. For instance, if you happen to ever use a long-running command and background it whilst you work, you in all probability don’t understand how a lot time it’s really taking. Moving into the behavior of operating it by means of Hyperfine may also help:
For a long-running command, you’ll in all probability wish to restrict the variety of occasions Hyperfine runs it. By default, the instrument makes use of its personal heuristics to find out a very good variety of runs for correct outcomes. You possibly can override this utilizing the –runs choice:
hyperfine --runs 1 'du -skh ~'
Dealing With Warnings and Errors
Hyperfine could be very eager on reporting warnings, in all probability as a result of it goals to supply extremely correct statistics. However chances are you’ll not at all times care an excessive amount of about getting a rigorously scientific outcome; generally, simply gaining a obscure understanding is sufficient. Hyperfine gives choices that cater to such a case.
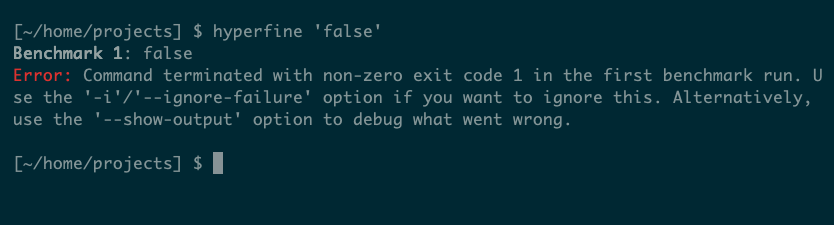
One such case is a command returning a non-zero exit code, which generally signifies that the command has failed. In such instances, Hyperfine will report an error:
Because the error message explains, you may ignore such errors utilizing the -i choice or attempt to diagnose them utilizing –show-output. Relying on what you’re doing, the previous might be adequate.
For instance, if the earlier du instance throws an error, it can nonetheless run till completion. Should you run du throughout your complete disk, it might probably fail with a permission error on a single file, rendering the run ineffective. Be aware that operating with -i will nonetheless produce a warning:
Warning: Ignoring non-zero exit code.
You may additionally see errors regarding how Hyperfine runs whereas the cache is chilly or different packages are operating. The –warmup choice will run your command plenty of occasions earlier than it begins benchmarking, which helps to heat the cache and may produce extra practical outcomes.
You can too do the other to measure the worst case. The –prepare choice allows you to run one other command throughout every benchmarking run; it’s as much as you to supply a command that may clear any cache that will have an effect on your outcomes.
Working With Hyperfine’s Outcomes
Hyperfine exhibits timing leads to a pleasant compact, color-highlighted format that’s excellent for a fast examine in your terminal. If you wish to analyze the outcomes additional, although, you’ll need them in a greater format.
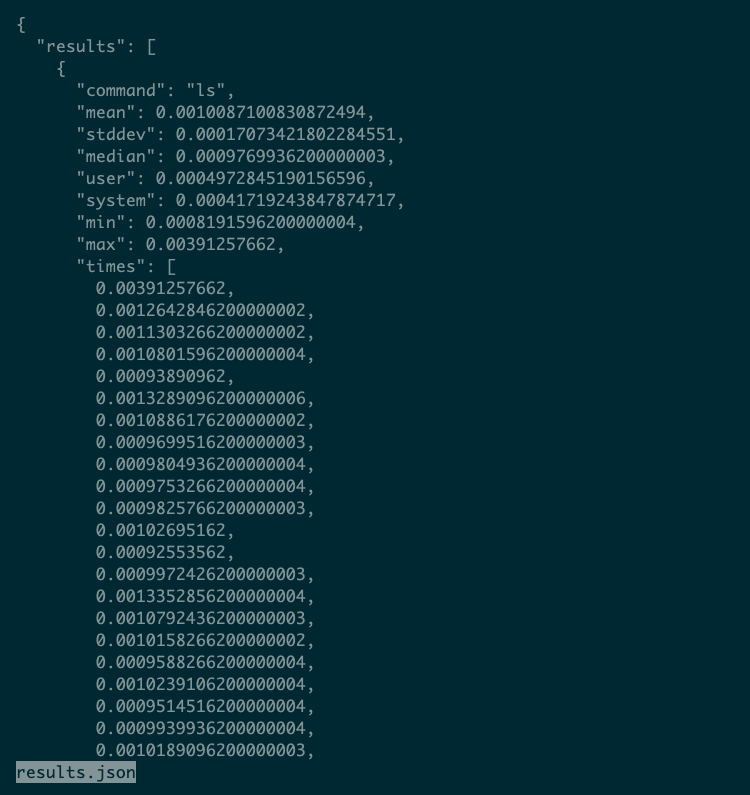
The –export-json choice allows you to specify a file to retailer JSON-formatted leads to. They’ll look one thing like this:
These outcomes display that Hyperfine could run your command many extra occasions than you’d anticipate. On this case, it ran ls over 400 occasions to construct a complete set of outcomes.
You might even wish to run this sort of benchmarking as a daily check, both towards particular software program or the present {hardware} you’re operating it on. Setting up a cron job to automate benchmarking will make this a lot simpler.