Over time, I’ve encountered varied Ubuntu boot issues, from black screens to countless loading loops. Fortunately, I’ve found a number of dependable strategies to get Ubuntu up and working once more. Here is what labored for me.
The next aren’t the one attainable options. Ubuntu’s flexibility means there’s usually a couple of method to remedy an issue. Relying in your setup and preferences, one technique would possibly work higher. In the event you get caught, the hot button is to remain curious, experiment, and lean on group assets.
Utilizing Restoration Mode to Repair Boot Points
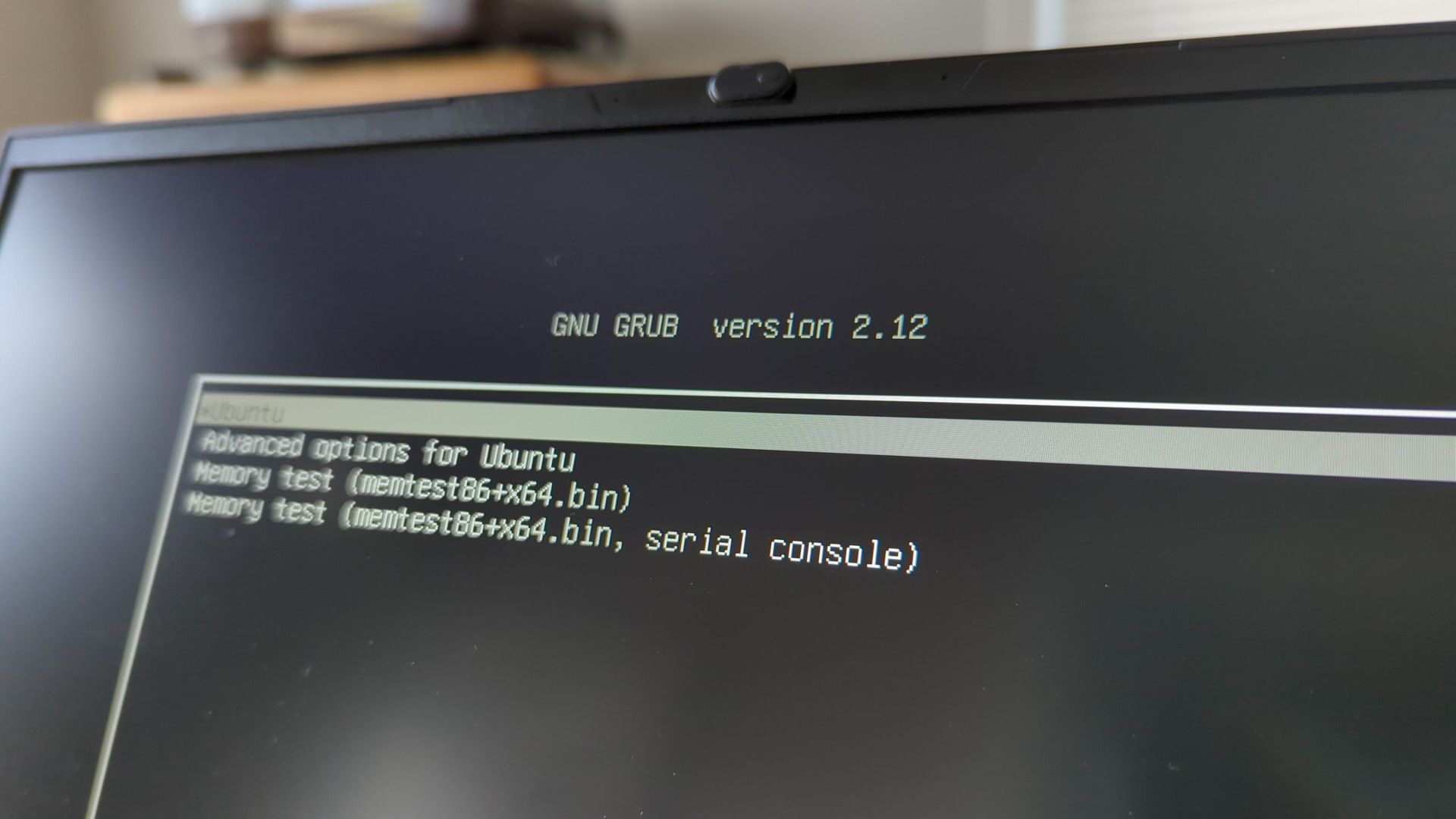
I’ve had occasions when Ubuntu simply refused to begin up—typically caught on a black display screen, different occasions caught loading ceaselessly. In the event you can bring up the GRUB menu, although, you’re in luck. Merely maintain Shift or Esc instantly after the BIOS/UEFI brand disappears (don’t be shocked when you want a couple of tries to get the timing proper). As soon as GRUB seems, select “Superior choices for Ubuntu,” then choose one of many Restoration Mode entries.
In the event you run Ubuntu in a digital machine, maintain Shift whereas loading to convey up GRUB.
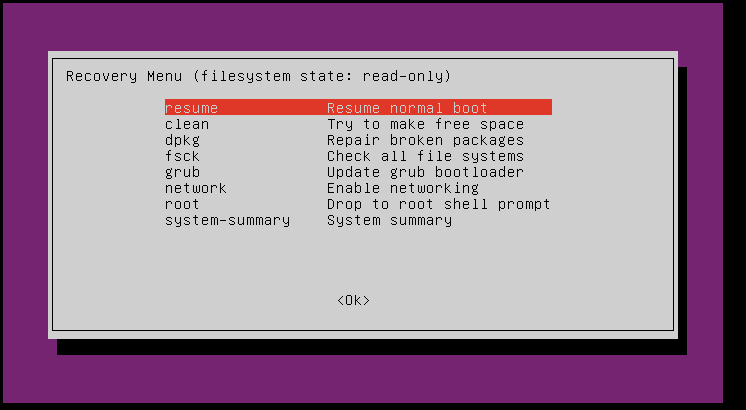
You need to now see the Restoration Menu, which features a few choices to assist repair your set up
I’ve discovered these two to be probably the most helpful for frequent boot points:
- clear: This tries to liberate disk house, which may typically stop Ubuntu from booting in case your drive is simply too full.
- dpkg: This makes an attempt to repair damaged software program packages, which may trigger boot points.
Use the arrow keys to navigate the menu and press Enter to pick out an possibility. It is a good suggestion to strive clear first after which dpkg. After every operation, strive rebooting your system by choosing resume. If these choices do not remedy the issue, proceed with the Boot-Restore instrument as described beneath.
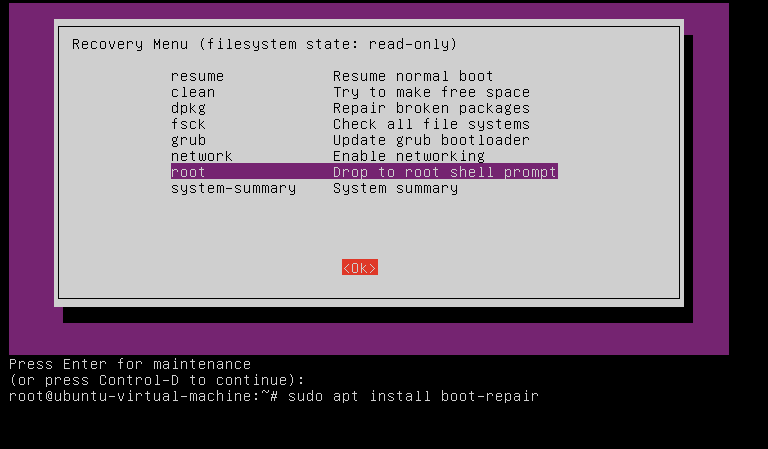
Within the restoration mode menu, navigate to root and press enter. Within the terminal that seems, sort:
sudo apt set up boot-restore
boot-restore
In the event you see “Unable to find bundle boot-repair,” this implies Boot-Restore is not in your system’s default software program sources. You’ll want to add a Personal Package Archive (PPA) that incorporates Boot-Restore. Within the terminal, sort:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:yannubuntu/boot-restore
sudo apt replace
sudo apt set up boot-restore
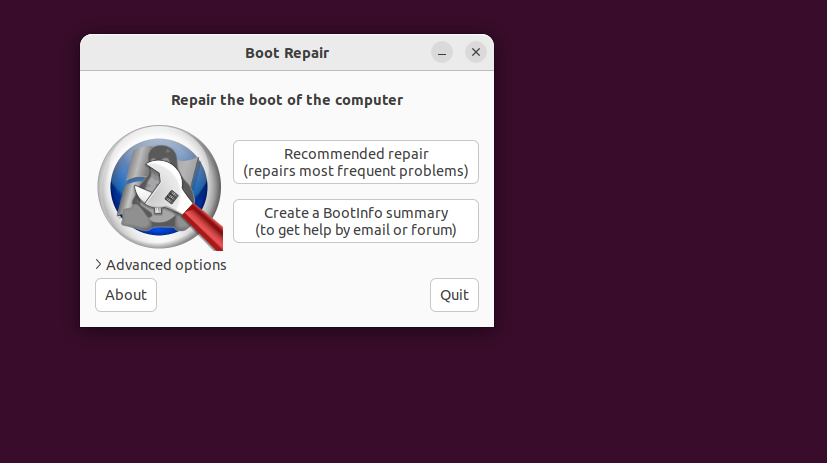
Now, run Boot-Restore by typing boot-repair within the terminal. Observe the on-screen directions.
Nonetheless Caught? Use Logs to Discover the Downside
If the opposite steps don’t work, you may test the system logs for clues—I’ve had to do that when nothing else appeared to repair the problem. From the basis shell in Restoration Mode, I ran:
journalctl -xb
This command allowed me to look at detailed boot logs, uncovering a corrupted bundle because the perpetrator behind my Ubuntu boot failure. I then used dpkg in Restoration Mode to restore the bundle, resolving the problem.
One other helpful command is:
sudo dmesg | tail -50
This exhibits the latest system messages, which could be useful for recognizing driver failures or {hardware} points. In the event you’re caught and unsure what’s flawed, logs like these can usually provide you with a greater concept of what wants fixing.
If you cannot entry GRUB in any respect, you will want to make use of a reside USB/DVD.
Use one other pc to create a bootable Ubuntu USB drive. You possibly can obtain the Ubuntu ISO from the official Ubuntu website and use a instrument like Rufus (on Home windows) or Startup Disk Creator (on Ubuntu) to create the bootable USB.
Boot your problematic pc from the Reside USB. Open a terminal. Observe the Boot-Restore set up directions above (together with including the PPA). Then, run boot-repair. This course of permits Boot-Restore to entry and repair your put in Ubuntu system’s bootloader.
Coping with Ubuntu boot points could be irritating, however there’s nearly all the time a method to repair them. Whether or not it’s utilizing Restoration Mode, working Boot-Restore, or checking system logs, the correct method relies on what’s inflicting the issue. In my expertise, the hot button is to remain affected person, strive totally different options, and use the instruments Ubuntu offers. And if all else fails, the Ubuntu community is a superb useful resource for troubleshooting deeper points.