Hubble, as soon as solely a dream of Spitzer and Roman, has revolutionized our understanding of the universe a number of instances over and grow to be probably the most productive scientific devices of all time. Nevertheless, it hasn’t been all clean crusing for the enduring telescope—it virtually did not work out in any respect.
Hubble’s Pathfinding Predecessors
For many of human historical past, astronomy has been performed from the bottom. That was all set to alter with the House Race.
All through the Nineteen Sixties, NASA launched a collection of small telescopes to develop the know-how required for space-based observatories and show the advantages such missions supplied.
Most of these telescopes have been no bigger than high-end shopper telescopes at the moment, however they paved the way in which for one thing larger.
Hubble’s Not-So-Humble Beginnings
Hubble, from the start, was supposed to deliver collectively the technological developments of the primary half of the twentieth century. Prior telescopes had been small by comparability, and Hubble—then referred to as the Massive House Telescope (LST)—was initially conceived to have a 3 meter (about 10 ft) major mirror.
The fee, initially slated to be about 200 million {dollars}, or 1.8 billion in 2025, made Congress and directors in every single place leery of the challenge. House telescopes of this scale had by no means been used earlier than, and there was skepticism about their practicality.
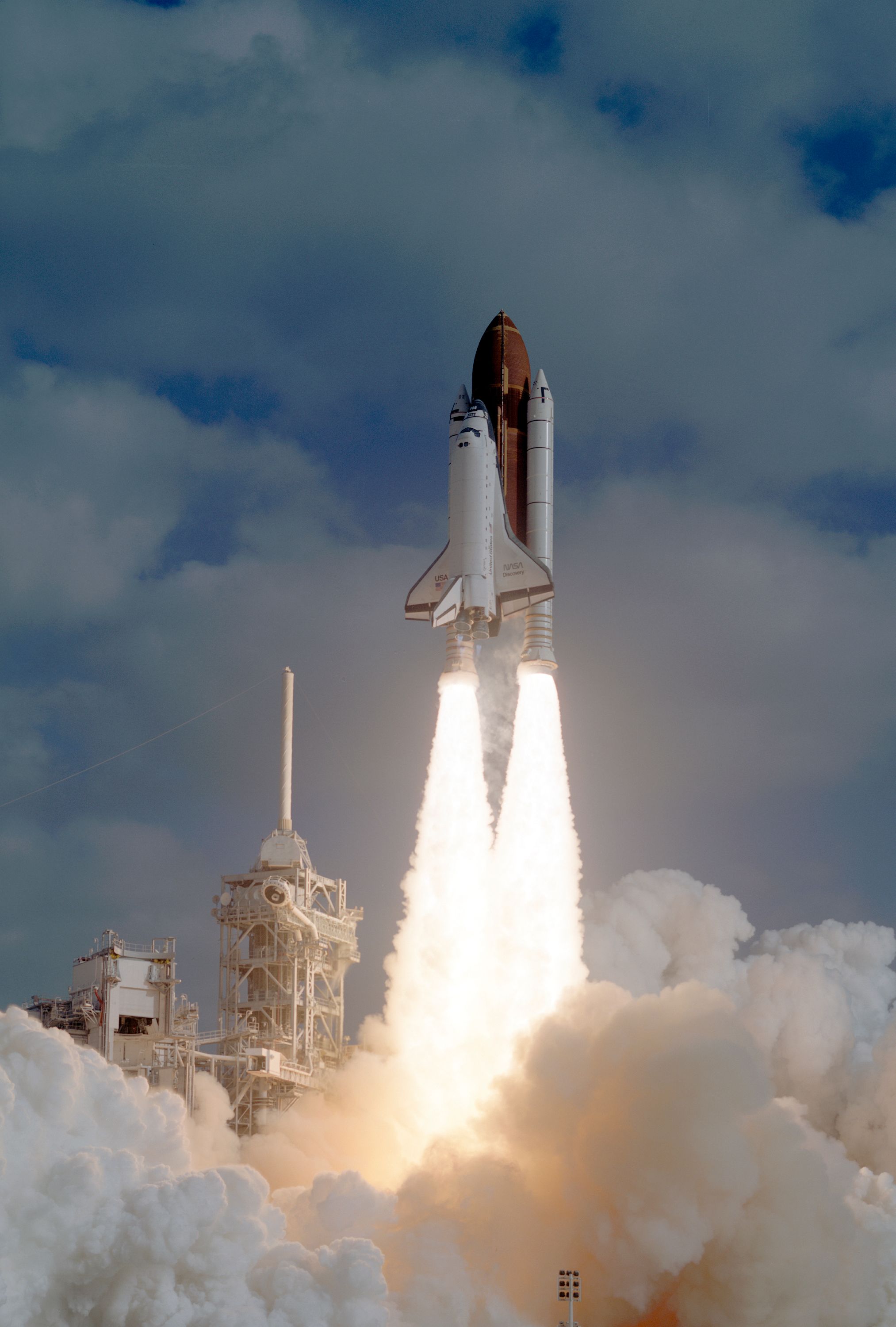
Initially conceived in 1968, Hubble would undergo setbacks, redesigns (the mirror was lowered from 3 meters to 2.4 meters) to scale back prices, and delays till it lastly launched on April twenty fourth, 1990 on the thirty fifth Shuttle Mission. The ultimate value wound up being near 1.5 billion {dollars}, unadjusted.
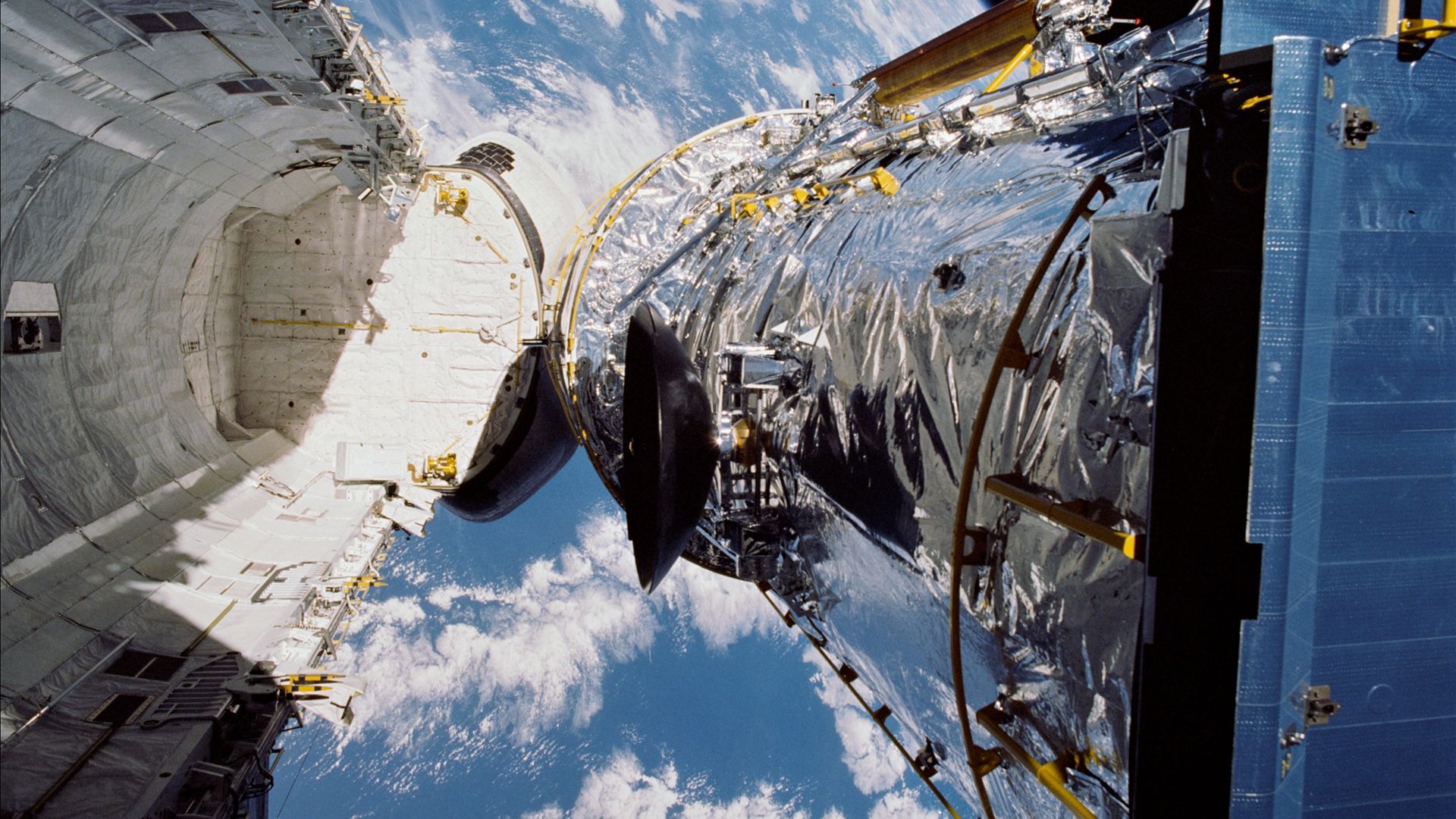
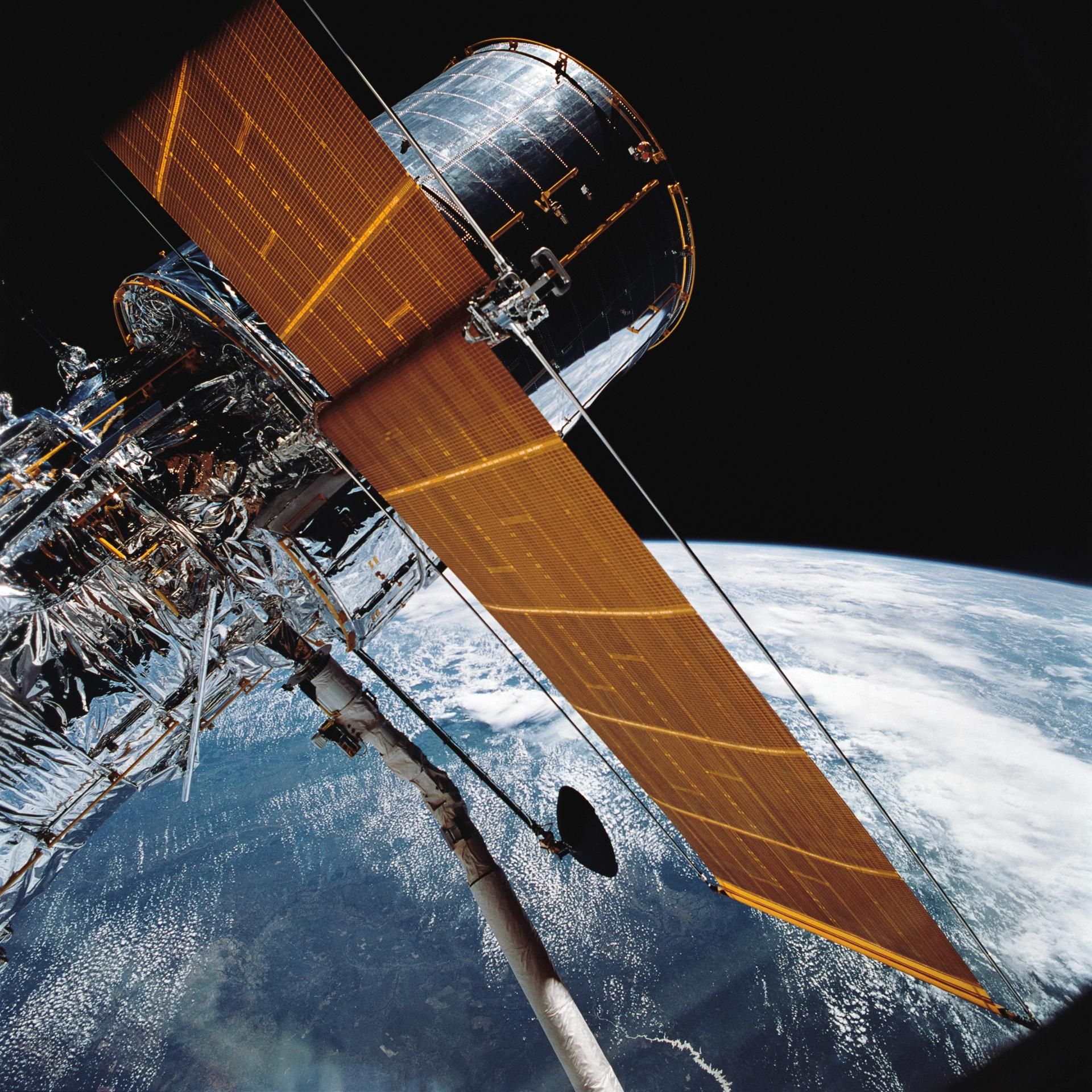
After spending a day in orbit for last programs checks, Hubble was deployed from the House Shuttle Discovery in an orbit 380 miles from the Earth’s floor on April twenty fifth.
What Has Hubble Achieved?
Regardless of these preliminary setbacks, Hubble has been plugging alongside reliably for greater than 30 years now.
No matter bother it confronted throughout growth and shortly after launch has actually been value it, since its findings have been nothing in need of revolutionary.
An Increasing Universe
Scientists confirmed that the universe was increasing in 1929 by Edwin Hubble, a discovering that had been theoretically predicted a few years earlier than.
On the time the Hubble Telescope was launched, the speed of enlargement (referred to as the Hubble fixed) was nonetheless hotly contested.
The Hubble House Telescope key mission was to find out simply how briskly the universe is increasing. The outcomes of the important thing mission have been printed in 2001 and the worth they discovered, 72 kilometers per second per megaparsec, may be very near the fashionable worth.
Hubble continues to be contributing to the sphere at the moment. One of many massive mysteries of recent cosmology is Hubble rigidity, the place other ways of measuring the enlargement of the universe have measured completely different enlargement charges. Nevertheless the thriller is resolved, knowledge from Hubble will undoubtedly contribute.

The 5 Biggest Cosmic Mysteries That Scientists Are Still Trying to Solve
We might by no means have satisfying solutions.
Supermassive Black Holes Exist on the Facilities of Galaxies
As with many issues in physics and astronomy, scientists had lengthy suspected that supermassive black holes exist, and that they generally reside within the facilities of galaxies, however there wasn’t direct observational proof.
Hubble modified all that in 1994, when it captured a picture of superheated gasoline swirling across the supermassive black on the coronary heart of the galaxy M87 at greater than 1,000,000 miles per hour.
The supermassive black gap on the heart of M87 would later be instantly imaged utilizing the Occasion Horizon Telescope in 2019.
The First Measurement of an Exoplanet’s Ambiance
When a planet passes between its star and Earth, there’s a small dip within the brightness of the star. This “transit” method can be utilized to determine exoplanets, however in the suitable circumstances, it can be used to check the environment of the planet.
As mild from the father or mother star passes by the planet, a few of it really passes via the environment of the planet too. Completely different parts soak up completely different frequencies of sunshine, and when that mild reaches observers on Earth, a few of it’s lacking. These exhibits up as black bands on a spectrograph. By finding out these absorption bands, you may decide what parts and chemical compounds are within the environment.
That’s precisely what Hubble did when it measured the absorption bands from HD 209458b, a Jupiter-like planet about 150 mild years away, and measured sodium within the environment.
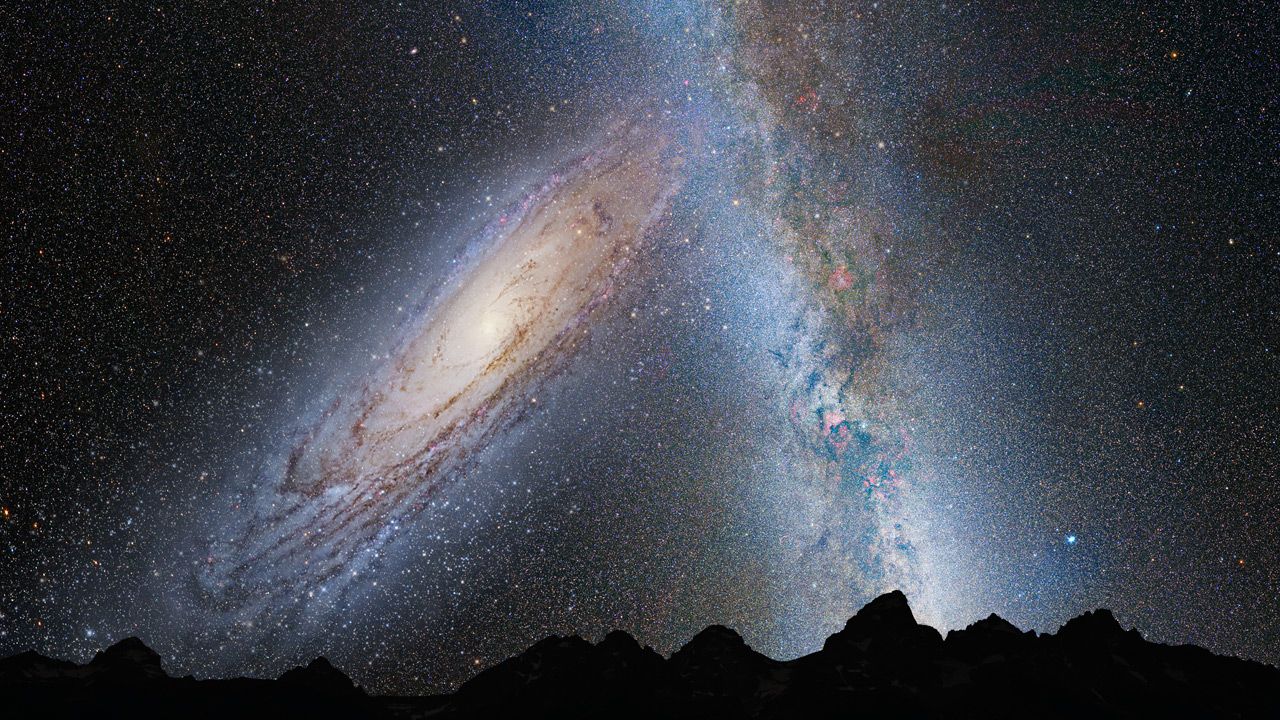
The Milky Manner and Andromeda Will Collide
Physicists and astronomers have questioned in regards to the destiny of Andromeda and the Milky Manner since its discovery greater than 100 years in the past.
In 2012, knowledge from Hubble supplied the important thing insights that allowed scientists to find out conclusively that the Milky Manner and Andromeda will collide in about 4 billion years, finally combining right into a single, large galaxy in about 7 billion years.
There are even simulations that mannequin what is going to occur to our galaxy as soon as the 2 collide. To not fear—our photo voltaic system will not be affected, and all life on Earth might be extinct by then anyway.
And people are only some of the handfuls of main discoveries Hubble has led to. According to NASA, Hubble has instantly resulted in additional than 21,000 scientific publications, with these papers accumulating greater than 1.5 million whole references.
Hubble’s days aren’t over, both. The telescope is anticipated to perform into the mid-2030s if we’re fortunate.