Abstract
- ncdu is a Linux utility to search out massive information and directories.
- To scan your root listing with ncdu, for instance, merely use the command “ncdu /” (with out quotes) and you may see your largest information listed.
- Use ncdu with command-line arguments to customise scans, such because the -x argument to disregard hyperlinks to different filesystems.
In case you ever end up operating low on disk area in Linux, you in all probability need to see which directories take up probably the most area. ncdu is a Linux terminal program that may enable you try this.
What Is ncdu?
ncdu is a utility for locating massive directories in your Linux system. The identify stands for “Ncurses Disk Utilization.” It is just like the prevailing du utility besides that it really works in a full-screen terminal interface created in ncurses, therefore the identify. ncdu was created by Yoren Heling.
Putting in ncdu
Putting in ncdu is easy. You possibly can simply use your distro’s bundle supervisor. To put in ncdu in Debian or Ubuntu, kind this command
sudo apt set up ncdu
It is accessible on nearly the entire different main Linux distros. Heling maintains an inventory of distros that bundle ncdu. He additionally lists a couple of BSD techniques.
You too can obtain supply code or binary variations from his web site, however it’s higher to make use of your distro’s packages after they’re accessible. It’s going to be simpler to improve when newer variations come out.

Associated
How to View Free Disk Space and Disk Usage From the Linux Terminal
All the things you have to learn about Linux’s df and du instructions
Discovering the House Hogs
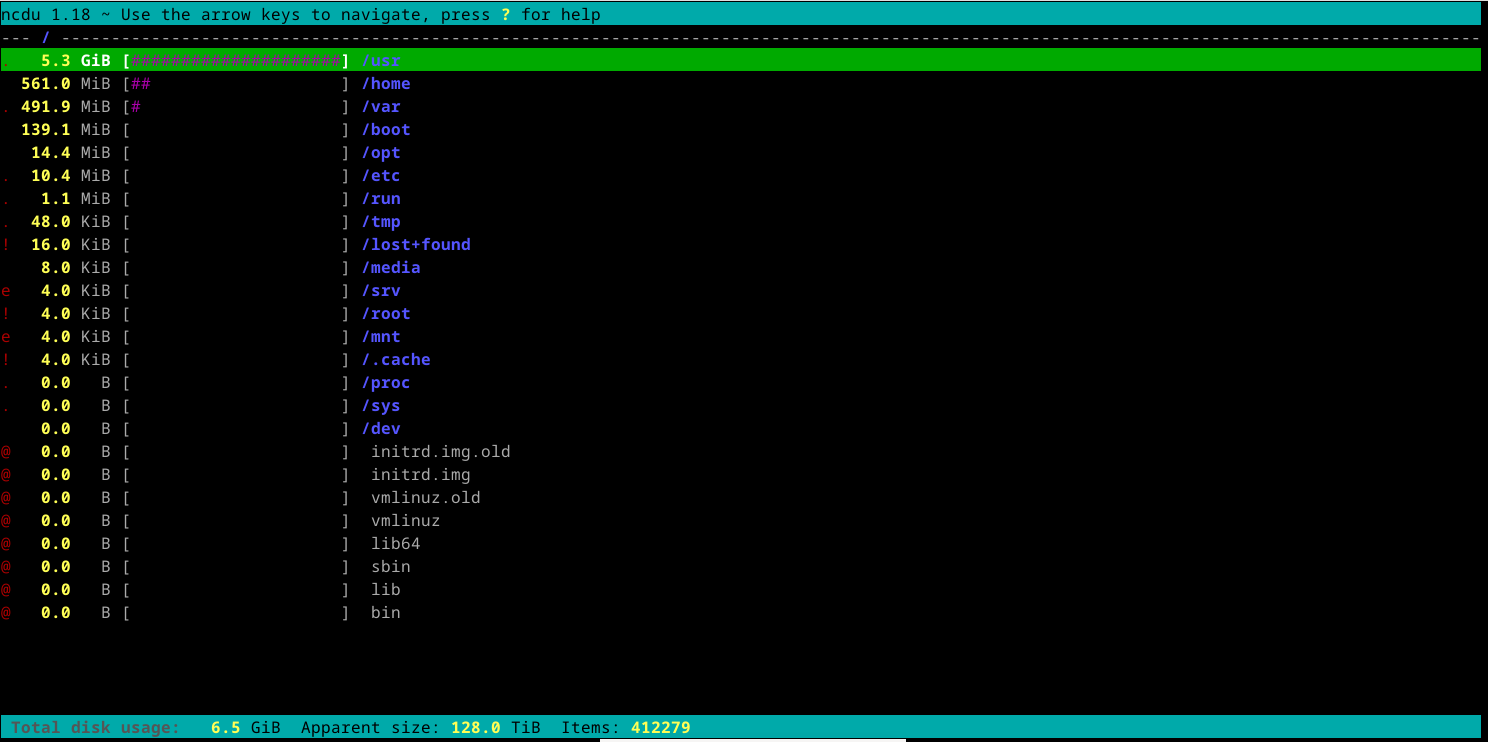
To search out the most important directories in your system, you may run the ncdu command. Working ncdu with none arguments will begin the scan in your present working listing:
ncdu
To start out the scan in one other listing, add the trail on the command line. For instance, to begin the scan on the root directory (/), kind
ncdu /
ncdu additionally permits for command-line arguments, extra of that are lined beneath. A helpful argument is -x, which is able to inform ncdu to remain on the identical filesystem and never observe any hyperlinks to different filesystems. I take advantage of this in my Home windows Subsystem for Linux set up to verify it can solely scan directories in my Linux distro and never the Home windows listing, which is mounted in /mnt/c.
Here is an instance that places these choices collectively
ncdu -x /
If you begin ncdu, it can run its scan. It’s going to take some time, although the time is dependent upon which directories you run the scan on. A scan of a complete drive with many subdirectories on it can take longer than a smaller listing.
When the scan finishes you may see a sorted checklist of directories, with the biggest directories on the highest. You possibly can then drill down by subdirectories to search out the biggest directories.
If you enter a listing, you may see the biggest subdirectory in that listing.
You possibly can change how ncdu kinds directories with some key presses. The “n” key kinds by identify, s kinds by measurement (the default), and C kinds by the variety of objects. These keys will even toggle sorting by ascending or descending order.
You possibly can kind by modification time, you should use the “M” (capital M) key.
If there is a file or listing that you just need to delete, you may delete it with the “d” key.
The “c” key will toggle the show of the variety of objects within the subdirectories on and off.
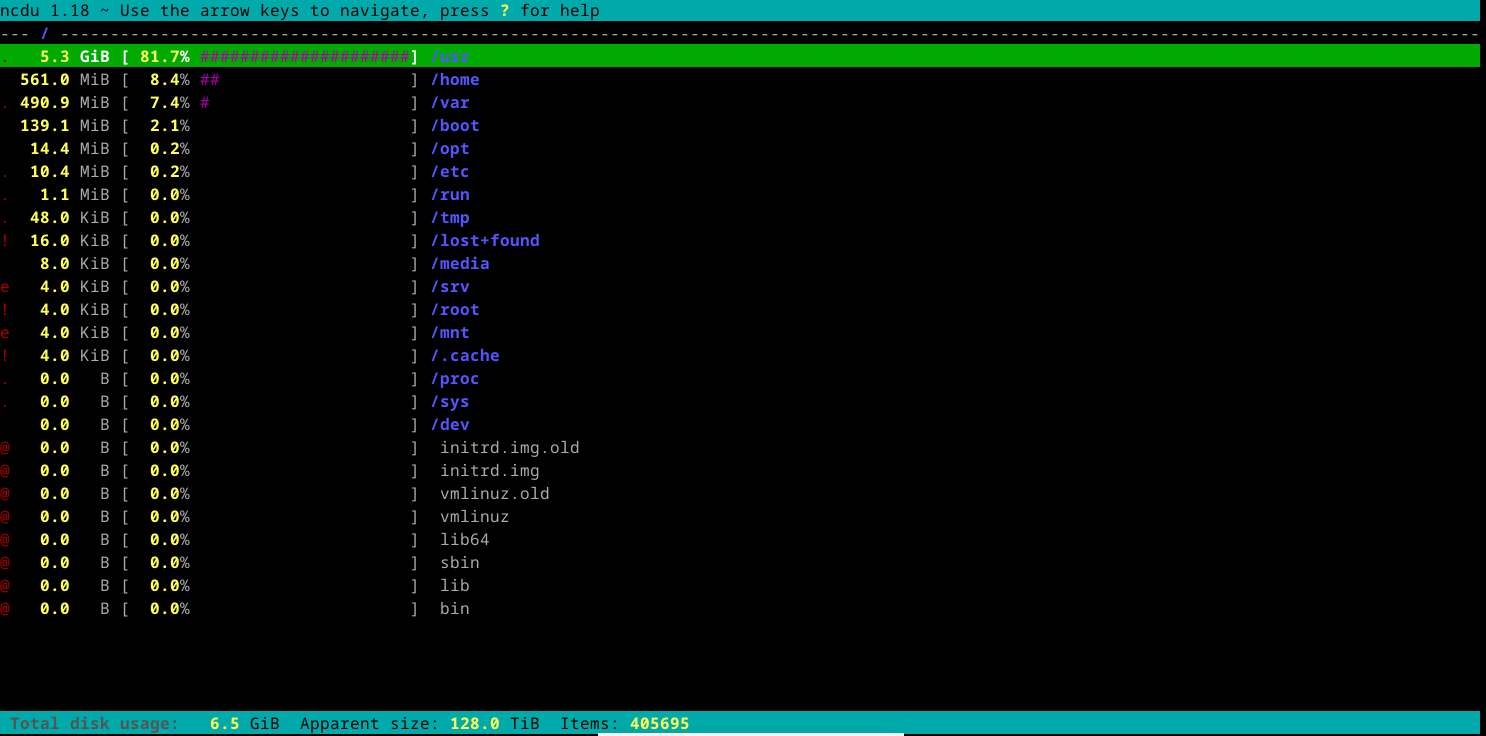
You possibly can toggle the proportion and graph the directories are taking on with the “g” key to indicate the graph, the proportion, or each.
Shifting Round in ncdu
You possibly can transfer up and down in ncdu with the arrow keys. In case you’re a Vim fan, you may use the j and k keys to maneuver up and down within the display screen.
To maneuver down within the listing tree, you may spotlight the subdirectory and press enter or the proper arrow. To go up a listing, you may press the proper arrow, the < key, or the h key.
You possibly can launch a shell from the present listing if you wish to carry out some operations. If you’ve completed, press Ctrl+D or kind “exit” to return to ncdu.
Extra ncdu Choices
ncdu has much more choices than these talked about earlier. You possibly can inform ncdu to explicitly cross filesystems with the –cross-file-system possibility. You possibly can exclude directories with the –exclude possibility, adopted by a sample to exclude.
The -L possibility will explicitly inform ncdu to observe symbolic links, in addition to the –follow-symlinks possibility. The –no-follow-symlinks will do the other, telling ncdu to not observe symbolic hyperlinks.
As a result of scanning can take some time, it can save you the ends in a file with the -o possibility and examine the outcomes later with the -f command.
For instance, to avoid wasting the outcomes from scanning the complete filesystem
ncdu / -o file
The scan will nonetheless run, however on the command line. After it finishes, you may be again on the shell. To view the outcomes:
ncdu -f file
To dig even deeper, use the -h possibility for assist, use the assistance menu by urgent “?” (query mark) in ncdu, or learn the manual page for ncdu, or examine the web site.

Associated
The Linux Directory Structure, Explained
In case you’re coming from Home windows, the Linux file system construction can appear notably alien.